As businesses expand globally, managing employee benefits across different countries becomes increasingly complex. Organizations must navigate a diverse array of healthcare frameworks, retirement schemes, and statutory leave regulations, all of which vary significantly by jurisdiction.
Failure to comply with local labor laws can result in substantial fines, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Employer of Record (EOR) services have emerged as a strategic solution to this challenge, acting as the legal employer while shouldering administrative and compliance responsibilities.
By leveraging EORs, companies gain access to localized benefits expertise, including health insurance negotiation, retirement plan administration, and statutory contribution management.
EOR providers maintain accurate records of social security, unemployment insurance, and workers’ compensation contributions on behalf of both employers and employees.
They also design competitive benefits packages, covering paid leave, maternity and paternity leave, and wellness programs, that help attract and retain top talent across borders.
This approach reduces HR complexity and administrative burden, enabling businesses to focus on core operations and growth strategies. Furthermore, EORs ensure that benefit offerings are aligned with market standards, fostering consistency and equity among global team members.
Ultimately, partnering with an EOR service simplifies global expansion by mitigating risk, lowering operational costs, and ensuring a seamless benefits experience for remote employees.
What Is An Employer Of Record (EOR)?
An Employer of Record (EOR) is a third-party provider that assumes the legal responsibilities of hiring employees on behalf of another company, particularly in foreign jurisdictions.
While your organization directs day-to-day tasks and performance management, the EOR becomes the official employer of record for payroll and statutory filings.
This includes withholding and remitting income taxes, social security contributions, and retirement fund payments in compliance with local regulations.
The EOR also administers employee benefits, such as health insurance, paid time off, and parental leave, through relationships with local providers. By centralizing these administrative tasks, an EOR mitigates legal risk, simplifies global expansion, and frees your HR team to focus on strategic growth.
The Role Of EORs In Managing Employee Benefits
EORs play a crucial role in administering employee benefits, ensuring that offerings are compliant with local regulations and competitive within the market. Here’s how they manage various aspects:

1. Health Insurance: EORs provide access to health insurance plans that comply with local laws and meet market standards.
They leverage their economies of scale and local partnerships to negotiate comprehensive coverage options—including medical, dental, and vision plans, often at reduced costs for employers and employees.
2. Retirement Plans: EORs facilitate contributions to retirement schemes, such as 401(k) plans in the U.S., pension schemes in Europe, and provident funds in Asia, ensuring accurate employer and employee deductions.
They handle plan setup, enrollment, compliance with ERISA and local regulations, and ongoing administration to maintain tax-advantaged status for all participants.
3. Paid Time Off (PTO): EORs manage vacation days, sick leave, and other PTO entitlements according to state and national labor laws, guaranteeing employees receive their full legally mandated time off.
They track accruals, usage, and carryover rules, and integrate PTO policies into payroll systems to ensure accurate compensation and robust recordkeeping.
4. Maternity and Paternity Leave: EORs ensure compliance with country-specific maternity and paternity leave regulations—such as the FMLA in the U.S. or paid parental leave schemes in Europe, by processing eligibility, documentation, and statutory benefit payments.
They coordinate with local social insurance agencies and employers to administer leave payroll, benefits continuation, and job protection provisions, minimizing legal risk and employee disruption.
5. Additional Benefits:
Many EORs offer supplementary benefits, such as employee wellness programs, tuition reimbursement, and employee assistance programs, which are designed to enhance engagement and retention.
By customizing these perks based on regional market standards and employee demographics, EORs help companies deliver competitive total rewards packages that support talent attraction and development.
Advantages Of Using EORs For Employee Benefits
Using an EOR to manage employee benefits offers strategic advantages for companies expanding into new markets. By outsourcing benefits administration to a compliant, regionally informed partner, businesses can reduce operational complexity while ensuring a competitive and legally sound employee experience.
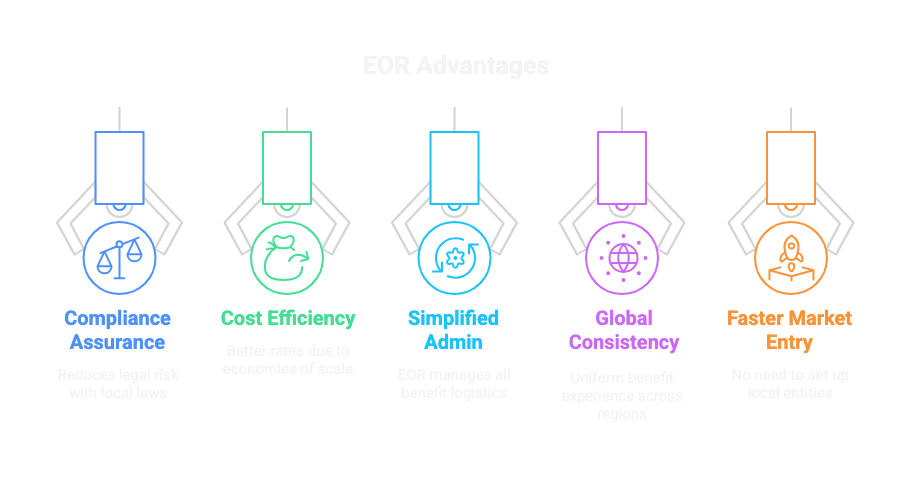
Compliance Assurance
EORs stay up to date with evolving labor laws and statutory benefit requirements in each country, ensuring that all offerings remain legally compliant. This reduces the risk of fines, disputes, or reputational damage due to non-compliance.
Cost Efficiency
By leveraging established provider networks and economies of scale, EORs can negotiate better rates on benefits packages than most companies can obtain independently. This helps businesses manage total compensation costs while still offering attractive benefits.
Simplified Administration
EORs handle the day-to-day management of benefits, including enrollment, documentation, and renewals, freeing up internal HR teams to focus on strategy and growth. Their platforms often integrate payroll and benefits, streamlining operations.
Global Consistency
EORs allow businesses to offer a consistent standard of benefits to employees across multiple countries while still meeting local legal requirements. This fosters equity and transparency within distributed teams.
Faster Market Entry
With benefit infrastructure already in place, EORs allow businesses to onboard employees and enter new markets quickly without the delays of setting up legal entities or local HR processes. This agility supports faster scaling and expansion.
Considerations When Choosing An EOR
Before partnering with an Employer of Record (EOR), companies must thoroughly evaluate multiple factors that impact compliance, costs, and service quality.
Assessing aspects such as the provider’s legal entity ownership in target countries, data protection standards, transparent pricing structures, and local expertise ensures the EOR aligns with your global expansion strategy and mitigates operational risks.
Legal Entity & Local Presence
An ideal EOR owns its own legal entities in the countries where it plan to hire, which minimizes reliance on third-party partners and reduces compliance risk.
This direct presence typically enables faster onboarding, more accurate payroll processing, and clearer lines of responsibility.
Compliance Expertise & Risk Management
Ensure the EOR demonstrates a strong commitment to compliance, with documented processes for adhering to local labor laws, tax regulations, and statutory benefits.
Look for third-party audit certifications or proof of past regulatory compliance to mitigate the risk of costly fines and legal liabilities.
Data Protection & Security Standards
Verify that the EOR maintains industry-standard data protection practices, such as ISO 27001 certification or comparable security frameworks, to safeguard sensitive employee information.
Confirm their infrastructure’s geographic location and data recovery plans to ensure compliance with GDPR and other regional privacy laws.
Transparent Pricing & Cost Structure
A reputable EOR provides clear, itemized pricing that details employer burden, service fees, and any variable charges (e.g., local statutory costs).
Beware of hidden fees and request examples of total cost breakdowns, validated by audited employer burden calculations, to prevent budget overruns.
Technology & Integration Capabilities
Assess the EOR’s technology platform for ease of use, real-time payroll dashboards, and seamless integration with your existing HRIS, ATS, and accounting systems.
Automated workflows for onboarding, reporting, and compliance reminders can drastically reduce administrative overhead and human error.
Geographic Coverage & Scalability
Confirm that the EOR covers both your current and future target markets, backed by on-the-ground experts who understand local employment nuances.
Evaluate their ability to rapidly scale up or down, handling seasonal fluctuations or sudden market entries, without service degradation.
Reputation, References & Customer Support
Research the EOR’s brand reputation through case studies, client testimonials, and independent review sites to gauge service quality and reliability. Ensure they offer dedicated account management and a clear escalation path for resolving issues quickly and effectively.
Benefits & Payroll Expertise
Verify that the EOR can administer local benefits packages, health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and accurately calculate payroll taxes and statutory contributions across jurisdictions.
Their expertise should include negotiating with local providers to deliver competitive rates and ensuring benefits compliance.
Reporting & Analytics
A robust reporting suite should offer detailed, exportable reports on headcount, payroll costs, benefits utilization, and compliance metrics to inform your business decisions. Look for customizable dashboards and automated alerts for tax filings, contract renewals, and regulatory changes.
Contract Terms & Flexibility
Review contract length, termination clauses, liability caps, and indemnification terms to ensure the agreement aligns with your risk appetite and growth plans. Favor providers offering flexible terms, such as month-to-month engagements or easy geographical add-ons, to adapt to evolving business needs.
Conclusion
Partnering with an EOR can dramatically streamline benefit management by centralizing administration under a single, compliant framework.
EORs maintain up-to-date knowledge of local labor and tax regulations, mitigating legal risks and ensuring statutory benefits like health insurance and retirement schemes are managed correctly.
By outsourcing payroll processing, tax filings, and benefits administration to an EOR, businesses avoid the complexities of establishing local entities and reduce operational overhead.
This delegation frees internal HR teams to concentrate on strategic initiatives, talent development, and core business growth rather than administrative tasks.
Additionally, EOR partnerships enhance competitiveness by leveraging provider networks to negotiate favorable benefit packages tailored to regional market standards.
Ultimately, working with an EOR ensures employees receive robust, compliant benefits across jurisdictions, supporting global expansion and fostering workforce satisfaction.