Expanding your business across borders is exciting, but it’s not without its challenges. Accessing new markets and tapping into global talent sounds like a growth dream, yet behind the scenes, it can quickly become a compliance and administrative nightmare.
When you’re hiring internationally without the support of an Employer of Record (EOR), suddenly you’re responsible for navigating complex local labor laws, setting up legal entities in every country, managing unfamiliar payroll systems, and trying to offer competitive benefits, often without having the right local knowledge.
And that’s just the paperwork. There are also time zone issues, cultural misunderstandings, and the challenge of keeping a globally dispersed team feeling connected and engaged.
In this guide, we’ll break down why expanding globally without an EOR can slow your growth, drain your resources, and increase compliance risks, and what you can do to manage these challenges more effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Hiring internationally without an EOR exposes companies to complex legal and compliance risks.
- Setting up local entities is time-consuming, costly, and often unnecessary for early-stage global expansion.
- Managing multi-country payroll, benefits, and taxes without local expertise leads to errors and potential penalties.
- Cultural differences, time zones, and poor onboarding processes hurt team collaboration and employee retention.
- Administrative overload from managing global HR in-house drains time and resources from core business growth.
- Partnering with an EOR enables faster, compliant, and cost-effective global hiring without setting up foreign entities.
What Is An Employer Of Record (EOR)?
If you’re new to the concept, an Employer of Record (EOR) is a partner that legally employs workers on your behalf in foreign countries. It takes care of payroll, benefits, tax compliance, and local labor regulations, so you can hire globally without setting up legal entities.
Learn more: What is an Employer of Record
Why Managing a Global Workforce Without an EOR is Risky?
Managing a global workforce without an Employer of Record (EOR) can expose businesses to a wide range of operational and legal complexities. Without centralized support, organizations face significant hurdles in maintaining compliance, consistency, and efficiency across international borders.
Risks of Global Hiring Without EOR
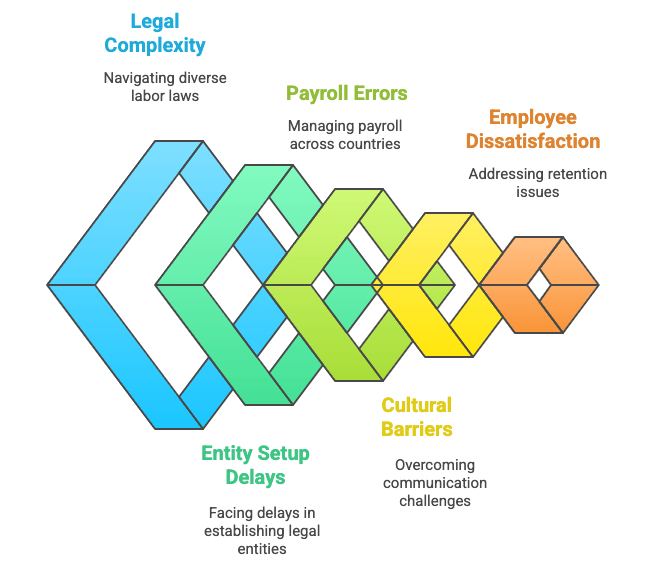
Compliance Challenges: Navigating Local Laws Without an EOR
One of the most significant challenges of managing a global workforce without an EOR is ensuring compliance with the diverse legal and regulatory frameworks in each country.
Every nation enforces its labor laws, tax obligations, employee protections, statutory benefits, working hours, termination rules, and reporting requirements.
These laws are not only complex but also subject to frequent changes, requiring constant monitoring and expertise. Without the guidance and infrastructure provided by an EOR, companies must take full responsibility for understanding and complying with these laws, often without having in-house legal experts with local knowledge.
This increases the risk of inadvertent violations, which can lead to serious consequences such as fines, employee lawsuits, back taxes, or even being barred from operating in that country.
Key Features Of This Challenge:
- Varying Employment Laws: From probationary periods to severance rules, every region has unique laws that must be followed precisely.
- Taxation and Social Contributions: Mismanaging income taxes, social security, or pension contributions can trigger audits or legal action.
- Worker Classification: Misclassifying employees as contractors can lead to retroactive penalties and benefits liabilities.
- Data Privacy and Employee Rights: Countries like those in the EU enforce strict data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR) that apply to employee information.
Why It’s Important:
Legal non-compliance can damage a company’s reputation, delay operations, and result in significant financial loss. More importantly, it can impact employee trust and retention, as workers expect fair treatment and security under local employment laws.
An EOR helps mitigate these risks by providing built-in compliance and local HR expertise, allowing companies to focus on business growth rather than legal pitfalls.
Why Setting Up Foreign Entities Slows Global Hiring?
To hire employees directly in a foreign country, businesses are typically required to establish a local legal entity, such as a subsidiary, branch office, or representative office, depending on the host country’s regulatory framework.
This step is not merely procedural; it is a legal prerequisite to operate, hire staff, and conduct business in a compliant manner within that jurisdiction.
Key Features:
- Entity Type Selection: Companies must choose the appropriate type of entity based on their intended business activities. For example, a subsidiary allows full business operations, while a representative office may restrict commercial activity.
- Registration Process: Setting up a legal entity involves registering with local authorities, tax agencies, and labor departments. This often requires submitting extensive documentation, securing local addresses, and appointing in-country directors or legal representatives.
- Banking & Tax Setup: Opening corporate bank accounts and registering for local tax IDs is mandatory, and can vary significantly in complexity by country.
- Ongoing Compliance: Once established, the entity must comply with regular filing requirements such as financial reporting, tax submissions, labor audits, and annual corporate governance obligations.
- Local Expertise Required: Navigating this process often necessitates local legal and accounting experts to avoid costly errors and ensure full compliance.
Why It’s Important:
Establishing a local entity is critical for companies seeking to build a permanent presence in a foreign market, manage payroll locally, and offer employee benefits aligned with national standards.
However, the process is resource-intensive, time-consuming, and can significantly delay market entry. Furthermore, any misstep in compliance or registration can result in legal penalties, reputational harm, or even restrictions on business operations.
With the complexities and risks associated with legal entity setup, companies can make more informed decisions about global expansion strategies, and may find alternative models like an Employer of Record (EOR) to be more agile and cost-effective for hiring international talent without long-term commitments.
Handling Global Payroll and Benefits Without Local Support
Administering payroll and benefits across multiple countries is a complex endeavor due to the diverse tax systems, currency fluctuations, and varying statutory requirements.
Without the support of an Employer of Record (EOR), companies must independently navigate these intricacies, increasing the risk of errors, compliance issues, and employee dissatisfaction.
Key Features:
- Diverse Tax Regulations: Each country has its tax structures, including income tax rates, social security contributions, and benefits mandates. Staying updated on these regulations is crucial to avoid penalties.
- Currency Exchange Management: Paying employees in different countries involves dealing with multiple currencies and exchange rates, which can affect budgeting and payroll accuracy.
- Compliance with Local Labor Laws: Adhering to specific labor laws, such as minimum wage, overtime rules, and termination procedures, is essential to prevent legal disputes.
- Benefits Administration: Managing diverse statutory benefits and entitlements across different countries requires a thorough understanding of local norms and legal requirements.
Why It’s Important:
Effectively managing international payroll and benefits is vital for maintaining compliance, ensuring employee satisfaction, and safeguarding the company’s reputation. Errors in payroll processing can lead to financial penalties, legal challenges, and loss of trust among employees.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, companies can streamline operations and focus on strategic growth initiatives.
How Cultural and Time Zone Barriers Impact Global Teams
Managing a diverse workforce across different time zones and cultures presents significant challenges, particularly in communication. Without localized HR support, fostering effective communication and a cohesive company culture becomes challenging.
Key Features:
- Diverse Communication Styles: Cultures vary in their communication approaches. High-context cultures (e.g., Japan, India) rely on implicit messages and non-verbal cues, whereas low-context cultures (e.g., the U.S., Germany) prefer direct and explicit communication. Misinterpretations can arise when team members are unaware of these differences.
- Language Differences: Even when a common language is used, variations in dialects, idioms, and proficiency levels can lead to misunderstandings. This can affect clarity in instructions, feedback, and collaboration.
- Non-Verbal Misinterpretations: Gestures, facial expressions, and body language can have different meanings across cultures. For instance, a gesture considered positive in one culture might be offensive in another. Such misinterpretations can hinder trust and rapport among team members.
- Time Zone Challenges: Coordinating meetings and project timelines across various time zones can lead to delays and reduced real-time collaboration, impacting team efficiency.
- Varied Attitudes Toward Hierarchy and Authority: Cultural differences influence perceptions of hierarchy. In some cultures, questioning authority is encouraged, while in others, it may be frowned upon. This can affect decision-making processes and team dynamics.
Why It’s Important:
Effectively managing cultural and communication barriers is crucial for enhancing collaboration, ensuring compliance, improving employee satisfaction, and boosting productivity within global teams. Understanding and respecting cultural differences fosters an inclusive environment that promotes better teamwork and innovation.
Clear communication aids in adhering to local labor laws and organizational policies, reducing the risk of legal issues. When employees feel understood and respected, job satisfaction and retention rates increase. Additionally, minimizing misunderstandings leads to more efficient workflows and project execution.
Why Onboarding and Offboarding Fail Without Local HR Expertise
Employee onboarding and offboarding are critical components of the employee life cycle that affect satisfaction, retention, and organizational security. Without an Employer of Record (EOR) managing localized compliance, companies may struggle to deliver a seamless, effective experience from hire to exit.
Key Features
• Standardized Onboarding Procedures: Uniform training, clear cultural communication, and prompt tool access accelerate new employee integration seamlessly.
• Localized Compliance and Customization: Tailored onboarding and offboarding processes meet local legal and cultural needs, avoiding compliance risks.
• Smooth Offboarding Protocols: Timely revocation of access and asset retrieval ensures data security and preserves organizational continuity.
Why It’s Important:
A seamless onboarding process directly influences employee satisfaction, productivity, and long-term retention by making new hires feel valued and well-prepared from day one.
Equally, robust offboarding safeguards the organization by reducing data vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance, and maintaining a positive employer brand, which is pivotal for future recruitment and employee referrals.
Managing Global Employee Benefits: Why It’s Harder Than You Think
Managing employee benefits and insurance across multiple countries without an Employer of Record (EOR) is a complex and resource-intensive endeavor.
Each nation has its own set of regulations, cultural expectations, and statutory requirements concerning benefits such as healthcare, retirement plans, paid leave, and social security contributions.
Without localized expertise, companies risk non-compliance, which can lead to legal penalties and damage to their reputation.
Key Challenges Without an EOR:
- Legal Compliance Risks: Navigating the intricate web of international labor laws is daunting. For instance, countries like France mandate 30 days of paid vacation annually, while others have different requirements. Failing to adhere to such laws can result in severe penalties.
- Administrative Burden: Managing diverse benefits programs requires significant administrative effort.
- Cultural Misalignment: Benefit expectations vary widely across cultures. What is considered a standard benefit in one country may be viewed as inadequate in another.
- Financial Implications: Mismanagement of benefits can lead to unexpected costs, including fines for non-compliance, increased turnover due to employee dissatisfaction, and inefficiencies in benefits administration.
Why It’s Important:
Offering competitive and compliant benefits is crucial for attracting and retaining talent in global markets. Employees are more likely to remain with companies that meet or exceed local benefits standards.
Moreover, proper benefits management ensures legal compliance, reduces administrative burdens, and enhances overall employee satisfaction.
Time, Cost, and Resource Strains of DIY Global Hiring
Managing the administrative tasks associated with international employment diverts time and resources from core business activities. Without the support of an EOR, HR teams may become overwhelmed, leading to inefficiencies and potential compliance oversights.
Key Features:
- Administrative Overload: Handling diverse international payroll systems, tax regulations, and employment laws requires significant time and expertise.
- Resource Diversion: Internal teams may need to allocate substantial resources to manage country-specific HR functions, detracting from strategic initiatives.
- Increased Risk of Errors: Without localized knowledge, the likelihood of compliance errors and administrative mistakes rises, potentially leading to legal and financial repercussions.
Why It’s Important:
Addressing time and resource constraints is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and focusing on growth. An EOR alleviates these burdens by managing administrative responsibilities, ensuring compliance, and allowing internal teams to concentrate on core business objectives.
This not only enhances productivity but also reduces the risk of costly errors associated with international employment management.
| Criteria | With EOR | Without EOR |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Compliance | Handled by EOR experts | You manage in-house |
| Entity Setup Required? | No | Yes |
| Payroll & Benefits | EOR manages locally | Complex, managed internally |
| Speed to Hire | Fast | Slow |
| Cost | Monthly service fee | High upfront costs |
| Employee Experience | Streamlined | Inconsistent |
Smarter Alternatives to Managing Without an EOR
Managing a global workforce without an Employer of Record (EOR) can be daunting, but there are strategic approaches to mitigate the challenges. By leveraging local expertise and adopting the right tools, companies can navigate the complexities of international employment.
- Partnering with Local Experts: Engaging local legal and HR consultants can help navigate country-specific employment laws and practices.
- Implementing Global HR Software: Utilizing technology platforms designed for international workforce management can streamline processes and improve compliance.
- Phased Expansion: Gradually entering new markets allows companies to build expertise and infrastructure incrementally, reducing risk.
Final Thoughts: Is Expanding Without an EOR Worth the Risk?
While expanding globally offers numerous opportunities, managing an international workforce without an Employer of Record (EOR) presents significant challenges. From legal complexities to administrative burdens, the risks and resource demands are substantial.
Companies must carefully assess their capabilities and consider strategic partnerships or solutions to ensure successful and compliant global operations.
Navigating the intricate landscape of international employment laws is a formidable task. Each country has its own set of labor regulations, tax codes, and compliance requirements, making it challenging for businesses to maintain adherence across multiple jurisdictions.
Missteps in compliance can lead to severe penalties, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Additionally, setting up legal entities in foreign countries demands significant time, resources, and local expertise.
Managing diverse payroll systems, benefits, and cultural expectations further complicates the process. Without the support of an EOR, companies may find themselves overwhelmed by these complexities, hindering their ability to focus on core business objectives and strategic growth.







